After almost two years of development, the open platform Openbot 0.8 has been launched. Designed to create mobile robots, the platform uses a standard Android smartphone as its base. Developed in the research unit of Intel, Openbot leverages the computing capabilities, GPS, gyroscope, compass, and cameras of a smartphone. The code is written in Swift and Java and is distributed under the MIT license. For more information, visit here.
The robot’s management software for analyzing the surrounding environment and enabling autonomous navigation is available as Android applications. Openbot is expected to be beneficial for educational purposes in robotics, rapid prototyping of mobile robots, and research related to autopilot and autonomous navigation.
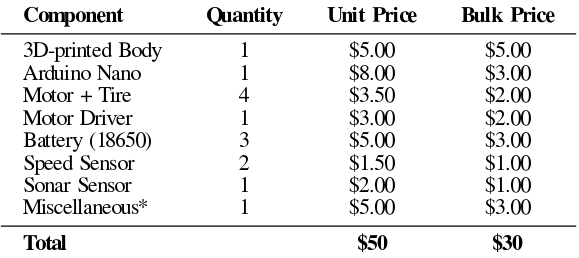
Openbot enables cost-effective experimentation with mobile robots, as it can be constructed using a mid-range smartphone along with additional components totaling about $50. The robot’s chassis and related parts for attaching the smartphone can be 3D printed based on the provided layouts. Alternatively, the frame can be crafted from cardboard or plywood. Movement is facilitated by four electric motors. For more details, refer to this link.
To control the motors, mounting equipment, additional sensors, and monitor the battery status, an ARDUINO Nano board with an ATMEGA328P microcontroller is utilized. This board connects to the smartphone via a USB port and supports the addition of speed sensors and Ultrasound Sonar. The robot can be remotely controlled through an Android app, a computer on the same Wi-Fi network through a web browser, or using a Bluetooth-enabled game controller (e.g., PS4, Xbox, or X3).