Group of researchers from Grazing Technical University (Austria), previously known to develop MDS attacks, Netspectre, Throwhammer and Zombiead, Posted New Attack method ( CVE-2021-3714 ) by third-party channels on the memory deduplication mechanism (Memory-Deduplication), which allows you to determine the presence in the memory of certain data, to organize a brief leakage of the memory contents or determine the memory layout to bypass the protection based on randomization of addresses (ASLR). From previously demonstrated options for attacks on the deduplication mechanism, a new method is characterized by an external host attack using the response time as a criterion to the responses sent by the HTTP / 1 and HTTP / 2 protocols. The ability to hold an attack is demonstrated for servers based on Linux and Windows.
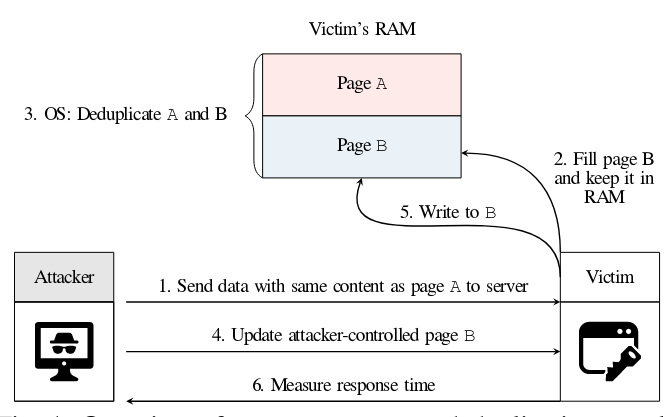
The attacks on the memory deduplication mechanism are used as a channel for leakage of information, the difference in processing the recording operation in situations where the change in the data leads to cloning a deedpouted memory page using the COPY-ON-WRITE mechanism (COW). In the process of operation, the kernel defines the same memory pages from different processes and combines them, displaying identical memory pages into one area of physical memory for storing only one copy. When you try to change one of the data processes associated with deduplicated pages, an exception arises (PageFaul) and using the COPY-ON-WRITE mechanism automatically creates a separate copy of the memory page that is secured by the process. Additional time is spent on copying, which may be a sign of changing data intersecting with another process.
Researchers have shown that the delay COW mechanism that occurs as a result of the operation can be caught not only locally, but also analyzing the change in the delivery time of the responses over the network. Several methods for determining the contents of memory from the remote host are proposed via an analysis of the time for executing requests for HTTP / 1 and HTTP / 2 protocols. To save the selected templates, typical Web applications are used that save information in requests in requests.
The general principle of attack is reduced to filling out the data page on the server, potentially repeating the contents of the memory page already available on the server. Then the attacker awaits the time required to perform the deduplication core and combining the memory page, after which it produces a change in the controlled duplicate data and estimates the reaction time to determine the success of the hit.