Google introduced “half-double “, new technique of Rowhammer class attacks that allow you to change the contents of individual dynamic memory bits (DRAM). The attack is reproduced on some modern DRAM chips, manufacturers of which achieved a decrease in cell geometry.
Recall that Rowhammer class attacks allow you to distort the contents of individual memory bits by cyclical reading data from neighboring memory cells. Since the DRAM memory is a two-dimensional array of cells, each of which consists of a capacitor and transistor, performing continuous reading of the same memory area leads to voltage fluctuations and anomalies that cause a small charge loss of adjacent cells. If the reading intensity is quite large, then the adjacent cell may lose a sufficiently large amount of charge and the next regeneration cycle will not have time to restore its original state, which will change the value of the value stored in the data cell.
To bypass the Half-Double-added DRAM manufacturers, the Half-Double method manipulates the fact that distortions are not limited to neighboring cells and distributed to other rows of memory cells, although to a lesser extent. Google engineers have shown that for serial strokes of memory “A”, “B and” C “, you can attack the” C “string with very intensive access to the” A “line and a small activity affecting the string” b “. Appeals to the string” B “During the attack, it activates a non-linear leakage of charges and allows you to use the” B “string in the role of transport to broadcast the Rowhammer effect from the string” A “on” with “
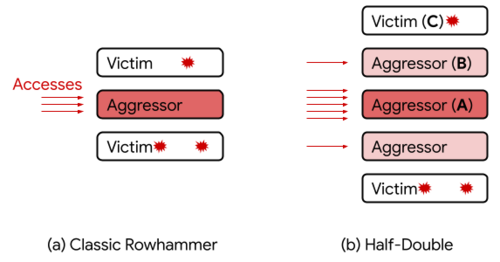
Unlike Trrespass attack, which manipulates flaws in various implementations of the TRR cell distortion mechanism (target Row Refresh), Half-Double attack is based on the physical properties of a silicon substrate. Half-Double shows that, probably leading to Rowhammer effects are the property of the distance between the cells, and not direct adjacent cells. With a decrease in the geometry of cells in modern chips, the radius of distortion is increasing. It is possible that the effect will be observed at a distance of more than two lines.